Difference between revisions of "Manual:Mudlet Packages"
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
{{TOC right}} | {{TOC right}} | ||
{{#description2:Mudlet packages - what they are and how to install / make them}} | {{#description2:Mudlet packages - what they are and how to install / make them}} | ||
| − | = What is a Mudlet | + | = What is a Mudlet Package? = |
| − | |||
| − | + | A Mudlet package is a collection of triggers, aliases, timers, etc that are bundled together in one file to perform a particular goal. This might be a Graphical User Interface for a particular MUD, or an automated bot that hunts down zombies. Packaging them all into one file allows them to be shared around to other players and Mudlet users. Mudlet packages contain XML files and other resources (images, sounds, etc), are in ZIP format, and commonly end with <code>.mpackage</code> but can also end in <code>.zip</code>. Upon installation the package is extracted and any scripts are assigned to the specific section in the Script Editor. Scripts installed from a package are highlight in brown in the Script Editor. | |
| − | + | = Where to find Mudlet Packages? = | |
| − | Check out the [https://forums.mudlet.org/viewforum.php?f=6 Scripts & Packages] section on Mudlet forums for an excellent selection of Mudlet packages. Those listings are also being transferred over to the [https://wiki.mudlet.org/w/Category:Mudlet_Package_Listing Mudlet Package Listing]. | + | |
| + | == via the Mudlet Package Repository == | ||
| + | |||
| + | The [https://github.com/Mudlet/mudlet-package-repository Mudlet Package Repository] is a collection of packages submitted by game developers, players and Mudlet fans alike. It is designed to be a central system for finding useful packages and scripts to enhance your gaming pleasure. While there is a vast array of packages available here, some scripters choose not to submit their work in which case you can find them somewhere else, see below. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == via the Web == | ||
| + | |||
| + | Check out the [https://forums.mudlet.org/viewforum.php?f=6 Scripts & Packages] section on Mudlet forums for an excellent selection of (sometimes) older Mudlet packages. Those listings are also being transferred over to the [https://wiki.mudlet.org/w/Category:Mudlet_Package_Listing Mudlet Package Listing] and the Mudlet Package Repository. | ||
Some Mudlet packages may also be exclusively available on your own game-specific website or forums, so make sure to check out what your game has to offer as well. | Some Mudlet packages may also be exclusively available on your own game-specific website or forums, so make sure to check out what your game has to offer as well. | ||
| − | = | + | Our [https://discordapp.com/invite/kuYvMQ9 Discord server] also has a Package channel where people can showcase their talents. Join our server, get assistance and talk all things Mudlet. |
| − | + | ||
| + | = Installing a Mudlet Package = | ||
| + | |||
| + | Packages must be installed into a chosen open profile. If you want to install a package in all your profiles you will need to do this for each profile separately (or use Modules - see below). | ||
| − | + | == via URL == | |
| + | |||
| + | {{note}} since 4.11+ | ||
| − | If you | + | If you have a web link to a package you can drag and drop that link onto an open profile and the package will get merged into that particular profile only. |
| − | == | + | == via Package Manager == |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | {{note}} since 4.8+ | |
| − | + | If you have a file on your computer you can drag and drop this onto an open profile as above. Alternatively, you can manage your packages via the Package Manager (Alt+O) from the toolbar. The Package Manager show details about installed packages on your system, and you can install and remove with the buttons at the bottom. The original download does not need to be kept as Mudlet has a copy of it once installed. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | [[File:Screenshot 20240925 130422.png|500px|center|Package Manager to install and remove Mudlet packages]] | |
| − | + | == via MPKG == | |
| − | + | If the package you require is available in the [https://github.com/Mudlet/mudlet-package-repository Mudlet Package Repository] you can use the command line tool called MPKG to install (and perform various other handy tasks like updates). | |
| − | + | <code>mpkg install package-name</code> | |
| − | |||
| − | + | If MPKG is not installed on your system, use one of the other methods to install it first, i.e. drag and drop [https://mudlet.github.io/mudlet-package-repository/packages/mpkg.mpackage this link] onto your profile. That link points to the latest version of the MPKG package. | |
| − | + | == via Command Line == | |
| − | + | Packages can also be installed via the command line using [[Manual:Technical Manual|Mudlet's API]]. | |
| − | + | <code>lua installPackage("https://<online package location>")</code> | |
| − | + | e.g. to install MPKG, Mudlet's command line package manager | |
| − | + | <code>lua installPackage("https://mudlet.github.io/mudlet-package-repository/packages/mpkg.mpackage")</code> | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | == | + | == via Game Server == |
| − | + | Packages can also be auto-installed from the MUD server (see [[Manual:ATCP_Extensions|ATCP extensions]] or [[Manual:GMCP_Extensions|GMCP extensions]] for more). You must have allowed the server to do this for your profile (turned on by default) from the profile Preferences (Alt+P). | |
| − | + | [[File:Screenshot 20240925 131702-1.png|500px|center|Allow server to install script packages]] | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | = | + | = What is a Mudlet Module? = |
| − | + | A Mudlet module is very similar to a Mudlet package - the only difference is how you import it: via the Module Manager (Alt+I) instead of the Package Manager (Alt+O), and what happens after: Mudlet will save the module back to the original file instead of the profile save file. This means the original XML or mpackage (in Mudlet 4.14+) will automatically get updated. Really useful if you're writing Mudlet code to share with others - you won't have to ever manually export it again, Mudlet will do it automatically for you! You can version your modules using Git using this way. | |
| − | + | You can also share a module across several profiles and automatically keep it in sync by installing the module in the relevant profiles and ticking the "sync" option in all of them. | |
| − | + | If you'd like your module to be loaded before all the scripts in a Mudlet profile, you can do that with the <code>-1</code> module priority. | |
| − | == | + | == Installing Modules == |
| − | [[ | + | == via Command Line API == |
| + | |||
| + | Modules can also be installed via the command line using [[Manual:Technical Manual|Mudlet's API]]. | ||
| − | + | <code>lua installModule("https://<online package location>")</code> | |
| − | + | == via Module Manager == | |
| − | + | If you have a module on your computer use the Module Manager (Alt+I) from the toolbar to install it. Modules can be uninstalled from the same interface. | |
| − | + | = Package Development = | |
| − | + | Have you made an awesome set of triggers or scripts for your game? Wish to share it with your fellow players and Mudlet users? Read on for information on how to create a package and get it distributed. | |
| − | + | == The Package Exporter == | |
| − | + | Mudlet provides the Package Exporter, found in the toolbar, for saving a selection of a profile's scripts to a file (mpackage). You can use this dialog to select the various scripts (and triggers, aliases, etc) that will become the basis of your new package. | |
| − | + | Exported settings are saved into an mpackage that can be imported using any of the supported installation methods (see [[Manual:Mudlet Packages#Installing_a_Mudlet_Package|Installing a Mudlet Package]]). | |
| − | |||
| − | Packages | + | [[File:ProfileExport-Start-Button.png|300px|center|Toolbox → Packages arrow]] |
| − | + | [[File:ProfileExport-Start-Menu.png|300px|center|upright=0.58|System Toolbox menu]] | |
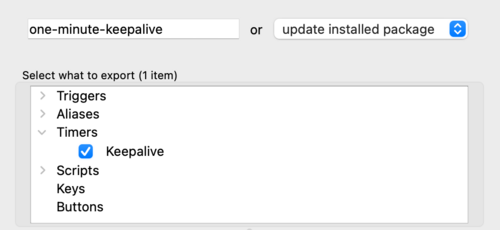
| − | + | Each package requires some metadata to explain what the package is all about. Choose a name (or if updating a package, select it from the dropdown list and it will populate the dialog). When selecting a name, try to ensure if is unique if possible. This helps players differentiate between two packages. | |
| − | + | Select the various triggers and scripts you wish to add to the package. | |
| − | [[File:ProfileExport-Form- | + | [[File:ProfileExport-Form-Name.png|500px|center]] |
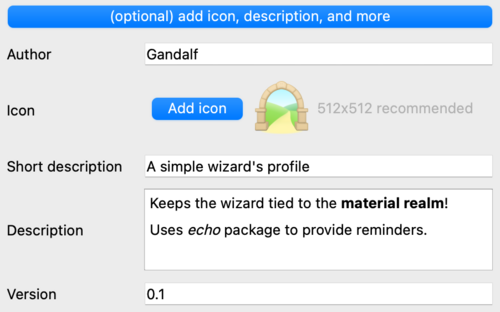
| − | + | Now add further detail by pressing the '''Describe your package''' button to define additional metadata and provide information to Mudlet users that choose to import your package. | |
| − | + | [[File:ProfileExport-Form-Options.png|500px|center|Make your package stand out]] | |
| − | |||
| − | + | The details allow setting: | |
| − | + | * author information, | |
| + | * an icon, 512x512 recommended, | ||
| + | * a short description; a one-liner for describing your package | ||
| + | * a description highlighting features, command usage and perhaps a screenshot, | ||
| + | * a version number. | ||
| − | + | This information is essential if you wish to be included in the [https://github.com/Mudlet/mudlet-package-repository Mudlet Package Repository]. | |
| − | + | You can use [https://guides.github.com/features/mastering-markdown/ Github-flavoured markdown] in the package description to give a nice presentation for the player. Try following the guidelines as mentioned in the pre-populated text. | |
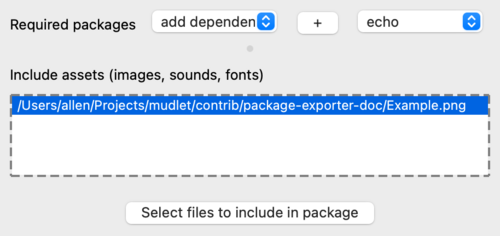
| − | + | If your package requires other Mudlet packages, add them under the Required packages dropdown. For example you might be creating a set of custom triggers for a game to use with <code>generic_mapper</code>, this would be considered a dependency otherwise your triggers won't work if another player does not have <code>generic_mapper</code> installed. | |
| − | |||
| − | + | {{note}} To remove a dependency that has already been selected and added, use CTRL+Delete (Linux/Windows) or FN+Backspace (MacOS). | |
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | + | [[File:ProfileExport-Form-References.png|500px|center|Include any dependencies]] | |
| − | + | Packages that reference local files such as images, sounds, fonts (.otf, .ttf) since Mudlet 3.0, will need to be declared in the final Assets section. Without these files the package may work locally but not on another players computer. These files will be copied into <code>getMudletHomeDir().."/"..packagename</code> upon installation, so your scripts can use them. | |
| − | |||
| − | For example, if your package is called "sipper" and you have health.png | + | For example, if your package is called "sipper" and you have health.png that has an image in it, you can place on a label like so: |
<syntaxhighlight lang="lua"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="lua"> | ||
| Line 130: | Line 133: | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | {note} To remove an included asset, select it from the list and use backspace (fn + delete on macOS) to remove it. | |
| + | |||
| + | Click '''Export''' to write the mpackage, which will be saved to your desktop by default. Use ''Select export location'' to pick a different destination. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:ProfileExport-Form-Export.png|500px|center|Set the .mpackage path]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Creating A Package by Hand == | ||
| + | |||
| + | While technically a package can be crafted by hand, we recommend you make use of the various unofficial tooling available. This will allow you to develop in your preferred IDE and create better diffs (eg. for use in Github). | ||
| + | |||
| + | * see [https://github.com/demonnic/muddler Muddler], a tool for creating Mudlet packages, | ||
| + | * see [https://github.com/Edru2/DeMuddler DeMuddler], a tool for deconstructing Mudlet packages, | ||
| + | |||
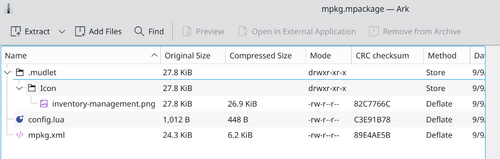
| + | {{note}} mpackages can be opened in any archive manager. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Screenshot 20240925 143545.png|500px|center|Structure of a mpackage.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Package and Module Best Practices == | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Manual:Best_Practices#Package_and_Module_best_practices|Best practices for Mudlet packages has its own page here.]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == MPKG and The Mudlet Package Repository == | ||
| + | |||
| + | The [https://github.com/Mudlet/mudlet-package-repository Mudlet Package Repository] is a collection of user-submitted packages centralized in one location. Packages like mappers, GUI's, tutorials and helpful functions, all created by Mudlet users. Think of it as a software manager for Mudlet. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <code>mpkg</code> is the command line package manager for Mudlet which allows you to install, remove, update and search for packages in this repository. <code>mpkg</code> links in to the [https://github.com/Mudlet/mudlet-package-repository Mudlet Package Repository] which provides users with a central location to find packages they would like to install without having to leave the Mudlet interface. | ||
| − | === | + | === Submitting A Package === |
| − | |||
| − | + | [https://github.com/Mudlet/mudlet-package-repository Mudlet Package Repository] is served via Github. Please check the [https://github.com/Mudlet/mudlet-package-repository repository] for instructions on how to get your package uploaded. | |
| + | |||
| + | === Migrating from GMCP to Mudlet Package Repository === | ||
| + | |||
| + | If your game currently serves up the a package via GMCP but you would prefer the package was hosted on the Mudlet Package Repository you will need a ''hook package'' to send via GMCP instead to tell Mudlet where to find your game package on the repository. | ||
| + | |||
| + | e.g. | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="lua"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="lua"> | ||
| − | + | -- define your MUD package | |
| + | local myMudPackage = "my-mud-package" | ||
| + | |||
| + | -- function to install or update your MUD package | ||
| + | local function installServerPackage() | ||
| + | local installedVersion = mpkg.getInstalledVersion(myMudPackage) | ||
| + | local repoVersion = mpkg.getRepositoryVersion(myMudPackage) | ||
| + | |||
| + | if not installedVersion then | ||
| + | mpkg.install(myMudPackage) | ||
| + | return | ||
| + | end | ||
| + | |||
| + | if semver(installedVersion) < semver(repoVersion) then | ||
| + | mpkg.upgrade(myMudPackage) | ||
| + | end | ||
| + | end | ||
| + | |||
| + | -- install mpkg if not already | ||
| + | local mpkgVersion = getPackageInfo("mpkg", "version") | ||
| − | + | if mpkgVersion == "" then | |
| + | installPackage("https://mudlet.github.io/mudlet-package-repository/packages/mpkg.mpackage") | ||
| + | -- wait a few seconds until mpkg is installed then check MUD package | ||
| + | tempTimer(5, function() installServerPackage() end) | ||
| + | else | ||
| + | installServerPackage() | ||
| + | end | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
| − | + | === Self-hosting and Mudlet Package Repository === | |
| − | < | + | If you still wish to self-host your package served up via GMCP, but want to be listed in the Mudlet Package Repository (for game visibility or other reasons) then you will need an ''installer package''. This would be as simple as [[Manual:Mudlet_Packages#The_Package_Exporter|creating a package with the Package Exporter]] and utilizing the API such that the package would simply install your self-hosted package; |
| − | + | ||
| + | <code>installPackage("https://<my game package location>")</code> | ||
| + | |||
| + | The cons of this method means that any updates to your package and notifying your users is up to you, as it will not be shared with the repository's update system. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
[[Category:Mudlet Manual]] | [[Category:Mudlet Manual]] | ||
Latest revision as of 11:05, 28 December 2024
What is a Mudlet Package?
A Mudlet package is a collection of triggers, aliases, timers, etc that are bundled together in one file to perform a particular goal. This might be a Graphical User Interface for a particular MUD, or an automated bot that hunts down zombies. Packaging them all into one file allows them to be shared around to other players and Mudlet users. Mudlet packages contain XML files and other resources (images, sounds, etc), are in ZIP format, and commonly end with .mpackage but can also end in .zip. Upon installation the package is extracted and any scripts are assigned to the specific section in the Script Editor. Scripts installed from a package are highlight in brown in the Script Editor.
Where to find Mudlet Packages?
via the Mudlet Package Repository
The Mudlet Package Repository is a collection of packages submitted by game developers, players and Mudlet fans alike. It is designed to be a central system for finding useful packages and scripts to enhance your gaming pleasure. While there is a vast array of packages available here, some scripters choose not to submit their work in which case you can find them somewhere else, see below.
via the Web
Check out the Scripts & Packages section on Mudlet forums for an excellent selection of (sometimes) older Mudlet packages. Those listings are also being transferred over to the Mudlet Package Listing and the Mudlet Package Repository.
Some Mudlet packages may also be exclusively available on your own game-specific website or forums, so make sure to check out what your game has to offer as well.
Our Discord server also has a Package channel where people can showcase their talents. Join our server, get assistance and talk all things Mudlet.
Installing a Mudlet Package
Packages must be installed into a chosen open profile. If you want to install a package in all your profiles you will need to do this for each profile separately (or use Modules - see below).
via URL
![]() Note: since 4.11+
Note: since 4.11+
If you have a web link to a package you can drag and drop that link onto an open profile and the package will get merged into that particular profile only.
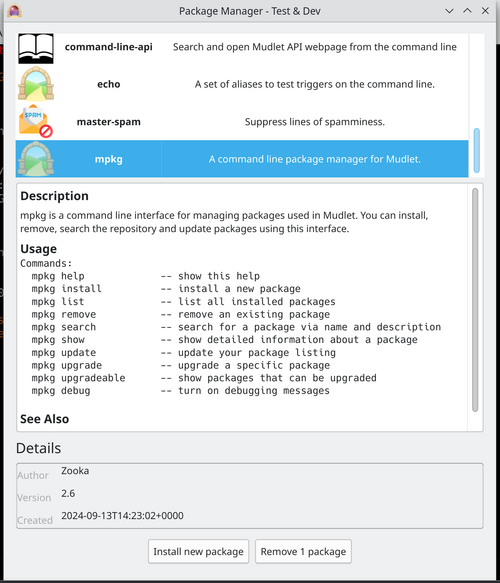
via Package Manager
![]() Note: since 4.8+
Note: since 4.8+
If you have a file on your computer you can drag and drop this onto an open profile as above. Alternatively, you can manage your packages via the Package Manager (Alt+O) from the toolbar. The Package Manager show details about installed packages on your system, and you can install and remove with the buttons at the bottom. The original download does not need to be kept as Mudlet has a copy of it once installed.
via MPKG
If the package you require is available in the Mudlet Package Repository you can use the command line tool called MPKG to install (and perform various other handy tasks like updates).
mpkg install package-name
If MPKG is not installed on your system, use one of the other methods to install it first, i.e. drag and drop this link onto your profile. That link points to the latest version of the MPKG package.
via Command Line
Packages can also be installed via the command line using Mudlet's API.
lua installPackage("https://<online package location>")
e.g. to install MPKG, Mudlet's command line package manager
lua installPackage("https://mudlet.github.io/mudlet-package-repository/packages/mpkg.mpackage")
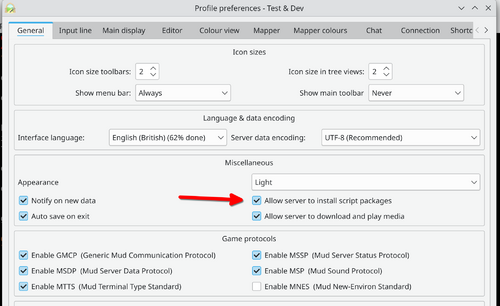
via Game Server
Packages can also be auto-installed from the MUD server (see ATCP extensions or GMCP extensions for more). You must have allowed the server to do this for your profile (turned on by default) from the profile Preferences (Alt+P).
What is a Mudlet Module?
A Mudlet module is very similar to a Mudlet package - the only difference is how you import it: via the Module Manager (Alt+I) instead of the Package Manager (Alt+O), and what happens after: Mudlet will save the module back to the original file instead of the profile save file. This means the original XML or mpackage (in Mudlet 4.14+) will automatically get updated. Really useful if you're writing Mudlet code to share with others - you won't have to ever manually export it again, Mudlet will do it automatically for you! You can version your modules using Git using this way.
You can also share a module across several profiles and automatically keep it in sync by installing the module in the relevant profiles and ticking the "sync" option in all of them.
If you'd like your module to be loaded before all the scripts in a Mudlet profile, you can do that with the -1 module priority.
Installing Modules
via Command Line API
Modules can also be installed via the command line using Mudlet's API.
lua installModule("https://<online package location>")
via Module Manager
If you have a module on your computer use the Module Manager (Alt+I) from the toolbar to install it. Modules can be uninstalled from the same interface.
Package Development
Have you made an awesome set of triggers or scripts for your game? Wish to share it with your fellow players and Mudlet users? Read on for information on how to create a package and get it distributed.
The Package Exporter
Mudlet provides the Package Exporter, found in the toolbar, for saving a selection of a profile's scripts to a file (mpackage). You can use this dialog to select the various scripts (and triggers, aliases, etc) that will become the basis of your new package.
Exported settings are saved into an mpackage that can be imported using any of the supported installation methods (see Installing a Mudlet Package).
Each package requires some metadata to explain what the package is all about. Choose a name (or if updating a package, select it from the dropdown list and it will populate the dialog). When selecting a name, try to ensure if is unique if possible. This helps players differentiate between two packages.
Select the various triggers and scripts you wish to add to the package.
Now add further detail by pressing the Describe your package button to define additional metadata and provide information to Mudlet users that choose to import your package.
The details allow setting:
- author information,
- an icon, 512x512 recommended,
- a short description; a one-liner for describing your package
- a description highlighting features, command usage and perhaps a screenshot,
- a version number.
This information is essential if you wish to be included in the Mudlet Package Repository.
You can use Github-flavoured markdown in the package description to give a nice presentation for the player. Try following the guidelines as mentioned in the pre-populated text.
If your package requires other Mudlet packages, add them under the Required packages dropdown. For example you might be creating a set of custom triggers for a game to use with generic_mapper, this would be considered a dependency otherwise your triggers won't work if another player does not have generic_mapper installed.
![]() Note: To remove a dependency that has already been selected and added, use CTRL+Delete (Linux/Windows) or FN+Backspace (MacOS).
Note: To remove a dependency that has already been selected and added, use CTRL+Delete (Linux/Windows) or FN+Backspace (MacOS).
Packages that reference local files such as images, sounds, fonts (.otf, .ttf) since Mudlet 3.0, will need to be declared in the final Assets section. Without these files the package may work locally but not on another players computer. These files will be copied into getMudletHomeDir().."/"..packagename upon installation, so your scripts can use them.
For example, if your package is called "sipper" and you have health.png that has an image in it, you can place on a label like so:
-- you don't have to worry about \ versus / for file paths - use / everywhere, Lua will make it work on Windows fine
setBackgroundImage("my health label", getMudletHomeDir().."/sipper/health.png"){note} To remove an included asset, select it from the list and use backspace (fn + delete on macOS) to remove it.
Click Export to write the mpackage, which will be saved to your desktop by default. Use Select export location to pick a different destination.
Creating A Package by Hand
While technically a package can be crafted by hand, we recommend you make use of the various unofficial tooling available. This will allow you to develop in your preferred IDE and create better diffs (eg. for use in Github).
- see Muddler, a tool for creating Mudlet packages,
- see DeMuddler, a tool for deconstructing Mudlet packages,
![]() Note: mpackages can be opened in any archive manager.
Note: mpackages can be opened in any archive manager.
Package and Module Best Practices
Best practices for Mudlet packages has its own page here.
MPKG and The Mudlet Package Repository
The Mudlet Package Repository is a collection of user-submitted packages centralized in one location. Packages like mappers, GUI's, tutorials and helpful functions, all created by Mudlet users. Think of it as a software manager for Mudlet.
mpkg is the command line package manager for Mudlet which allows you to install, remove, update and search for packages in this repository. mpkg links in to the Mudlet Package Repository which provides users with a central location to find packages they would like to install without having to leave the Mudlet interface.
Submitting A Package
Mudlet Package Repository is served via Github. Please check the repository for instructions on how to get your package uploaded.
Migrating from GMCP to Mudlet Package Repository
If your game currently serves up the a package via GMCP but you would prefer the package was hosted on the Mudlet Package Repository you will need a hook package to send via GMCP instead to tell Mudlet where to find your game package on the repository.
e.g.
-- define your MUD package
local myMudPackage = "my-mud-package"
-- function to install or update your MUD package
local function installServerPackage()
local installedVersion = mpkg.getInstalledVersion(myMudPackage)
local repoVersion = mpkg.getRepositoryVersion(myMudPackage)
if not installedVersion then
mpkg.install(myMudPackage)
return
end
if semver(installedVersion) < semver(repoVersion) then
mpkg.upgrade(myMudPackage)
end
end
-- install mpkg if not already
local mpkgVersion = getPackageInfo("mpkg", "version")
if mpkgVersion == "" then
installPackage("https://mudlet.github.io/mudlet-package-repository/packages/mpkg.mpackage")
-- wait a few seconds until mpkg is installed then check MUD package
tempTimer(5, function() installServerPackage() end)
else
installServerPackage()
endSelf-hosting and Mudlet Package Repository
If you still wish to self-host your package served up via GMCP, but want to be listed in the Mudlet Package Repository (for game visibility or other reasons) then you will need an installer package. This would be as simple as creating a package with the Package Exporter and utilizing the API such that the package would simply install your self-hosted package;
installPackage("https://<my game package location>")
The cons of this method means that any updates to your package and notifying your users is up to you, as it will not be shared with the repository's update system.