Difference between revisions of "Standards:GMCP Authentication"
(Externalise OAuth and support accounts) |
|||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
Sent in response to <code>Client.Supports.Set</code>, it informs the client of the supported authentication methods: | Sent in response to <code>Client.Supports.Set</code>, it informs the client of the supported authentication methods: | ||
| − | *<code>type</code>: | + | *<code>type</code> (array of strings, required): indicates the supported method(s), which is one or more of: |
| − | **<code>password-credentials</code>: | + | **<code>password-credentials</code>: traditional username/password login. |
| − | ** <code>oauth | + | ** <code>oauth</code>: OAuth-based login. |
| − | * | + | *<code>location</code> (string, required if <code>type</code> is <code>oauth</code>): openid-configuration location. See https://openid.net/specs/openid-connect-discovery-1_0.html |
| − | |||
| − | Since multiple flows can be supported by a server the <code>type</code> array shall be ordered in the descending order of preference by the server. | + | Since multiple flows can be supported by a server, the <code>type</code> array shall be ordered in the descending order of preference by the server. For example, if the server supports only the credentials flow: |
Client.Authenticate.Default {"type": ["password-credentials"]} | Client.Authenticate.Default {"type": ["password-credentials"]} | ||
| − | If the server supports both | + | If the server supports both OAuth and credentials and prefers OAuth: |
| − | Client.Authenticate.Default {"type": ["oauth | + | Client.Authenticate.Default {"type": ["oauth", "password-credentials"], "location": "<nowiki>https://example.com/.well-known/openid-configuration</nowiki>" } |
===== Client.Authenticate.Result ===== | ===== Client.Authenticate.Result ===== | ||
Sent in response to <code>Client.Authenticate.Credentials</code>, it informs the client of the success or failure of the credentials-based login. | Sent in response to <code>Client.Authenticate.Credentials</code>, it informs the client of the success or failure of the credentials-based login. | ||
| − | * <code>success</code>: (boolean) Indicates whether the authentication attempt was successful. | + | * <code>success</code>: (boolean, required) Indicates whether the authentication attempt was successful. |
| − | * <code>message</code>: (string) required string if the login wasn't successful: a human-readable message explaining the result, such as "Invalid credentials" or "Character not found". | + | * <code>message</code>: (string, required if <code>success</code> is false) required string if the login wasn't successful: a human-readable message explaining the result, such as "Invalid credentials" or "Character not found". |
==== Client-side ==== | ==== Client-side ==== | ||
===== Client.Authenticate.Credentials ===== | ===== Client.Authenticate.Credentials ===== | ||
| − | + | After receiving <code>Client.Authenticate.Default</code> with <code>type</code> as <code>password-credentials</code>, the client sends the character name and password for traditional login. | |
| + | |||
| + | * <code>account</code> (string, required): character name or the player account name. For games that implement both player and character names, the character name would be handled in plain text outside of this spec. | ||
| + | * <code>password</code> (string, required): character password. Servers are encouraged to implement [[Manual:Supported Protocols#Secure connection .28TLS.29|TLS over telnet]] to allow secure transmission of passwords. | ||
| Line 50: | Line 52: | ||
[[File:GMCP authenticate flow.png|none|thumb|780x780px|Example password flow ([https://gist.github.com/vadi2/6fcc05500823122143a5d45c43915ff0 source])]] | [[File:GMCP authenticate flow.png|none|thumb|780x780px|Example password flow ([https://gist.github.com/vadi2/6fcc05500823122143a5d45c43915ff0 source])]] | ||
| − | |||
| − | Specific details for | + | |
| + | '''OAuth Flows''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Specific details for the OAuth flow will be detailed once it is worked out with the community. | ||
=== Implementation Considerations === | === Implementation Considerations === | ||
Revision as of 13:11, 17 February 2024
GMCP Extension for MUD Client Authentication
This document defines a new GMCP extension to enable MUD clients to send credentials and perform authentication using GMCP messages instead of in-band login commands. It also includes optional support for OAuth authorization flows.
Rationale
Different MUDs have diverse login command formats, making it challenging for MUD clients to handle login consistently. This extension provides a standardized way to exchange authentication information through GMCP, simplifying client development and improving compatibility. Additionally, the extension supports OAuth authorization flows, allowing clients to leverage external identity providers for login.
Design
The extension introduces a new namespace called Client.Authenticate with the following commands:
Server-side
Client.Authenticate.Default
Sent in response to Client.Supports.Set, it informs the client of the supported authentication methods:
type(array of strings, required): indicates the supported method(s), which is one or more of:password-credentials: traditional username/password login.oauth: OAuth-based login.
location(string, required iftypeisoauth): openid-configuration location. See https://openid.net/specs/openid-connect-discovery-1_0.html
Since multiple flows can be supported by a server, the type array shall be ordered in the descending order of preference by the server. For example, if the server supports only the credentials flow:
Client.Authenticate.Default {"type": ["password-credentials"]}
If the server supports both OAuth and credentials and prefers OAuth:
Client.Authenticate.Default {"type": ["oauth", "password-credentials"], "location": "https://example.com/.well-known/openid-configuration" }
Client.Authenticate.Result
Sent in response to Client.Authenticate.Credentials, it informs the client of the success or failure of the credentials-based login.
success: (boolean, required) Indicates whether the authentication attempt was successful.message: (string, required ifsuccessis false) required string if the login wasn't successful: a human-readable message explaining the result, such as "Invalid credentials" or "Character not found".
Client-side
Client.Authenticate.Credentials
After receiving Client.Authenticate.Default with type as password-credentials, the client sends the character name and password for traditional login.
account(string, required): character name or the player account name. For games that implement both player and character names, the character name would be handled in plain text outside of this spec.password(string, required): character password. Servers are encouraged to implement TLS over telnet to allow secure transmission of passwords.
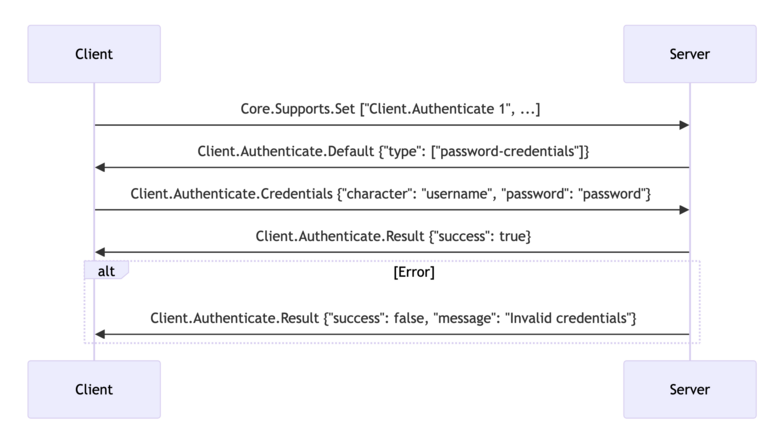
Example Flow (Password Credentials):
- Client connects and sends:
Core.Supports.Set ["Client.Authenticate 1", ...] - Server responds with:
Client.Authenticate.Default {"type": ["password-credentials"]} - Client sends:
Client.Authenticate.Credentials {"character": "username", "password": "password"} - Server validates credentials and performs login.
OAuth Flows
Specific details for the OAuth flow will be detailed once it is worked out with the community.
Implementation Considerations
- This extension should be implemented according to the GMCP protocol specifications.
- Messages should be well-formatted JSON objects.
- Servers should validate incoming authentication information securely.
- Clients should handle potential errors and server responses gracefully.
Conclusion
This GMCP extension provides a standardized and flexible approach to MUD client authentication, improving compatibility and enabling support for OAuth authorization flows. By adopting this extension, MUD developers and client developers can simplify login processes and enhance user experience.
Note: This is a draft proposal, and further community input and refinement may be necessary before finalizing the specification. Additionally, the specific details of OAuth flow support require input from the community to be defined.